In the rapidly evolving world of drones, long-range video transmission has become a key feature for both hobbyists and professional UAV operators. Whether you’re a drone pilot interested in capturing breathtaking aerial photography or a professional using drones for surveying, inspection, or FPV racing, understanding long-range drone video transmitters is essential. This article explores everything you need to know about long-range drone video transmitters, including technology, selection criteria, best practices, and potential challenges.
Understanding Drone Video Transmitters
A drone video transmitter (VTX) is an electronic device installed on a drone to send live video signals from the drone’s onboard camera to the ground-based receiver, usually connected to a monitor, FPV goggles, or a recording device. The quality and reliability of the video feed depend largely on the transmitter’s capabilities, including its transmission power, frequency band, antenna design, and latency.
For long-range applications, a video transmitter must be capable of sending a stable, high-quality signal over several kilometers, often in environments with potential interference from buildings, other electronics, or weather conditions.
Key Features of Long-Range Drone Video Transmitters
When selecting a long-range drone video transmitter, consider the following key features:
1. Transmission Power (mW)
Transmission power is one of the most critical factors for range. Most drone VTX units allow you to select different power levels, typically ranging from 25mW to 1200mW. Higher power provides longer transmission range but may also consume more battery and generate more heat. In many countries, regulatory bodies limit the maximum allowed transmission power, so ensure compliance with local laws.
2. Frequency Bands
Long-range VTX units typically operate on 2.4GHz or 5.8GHz bands:
-
2.4GHz: Offers longer range and better penetration through obstacles but can be more crowded due to Wi-Fi and other devices.
-
5.8GHz: Provides higher video quality with lower interference but has shorter effective range and is more affected by obstacles.
Some advanced VTX models support multi-band operation, allowing pilots to switch frequencies dynamically to avoid interference.
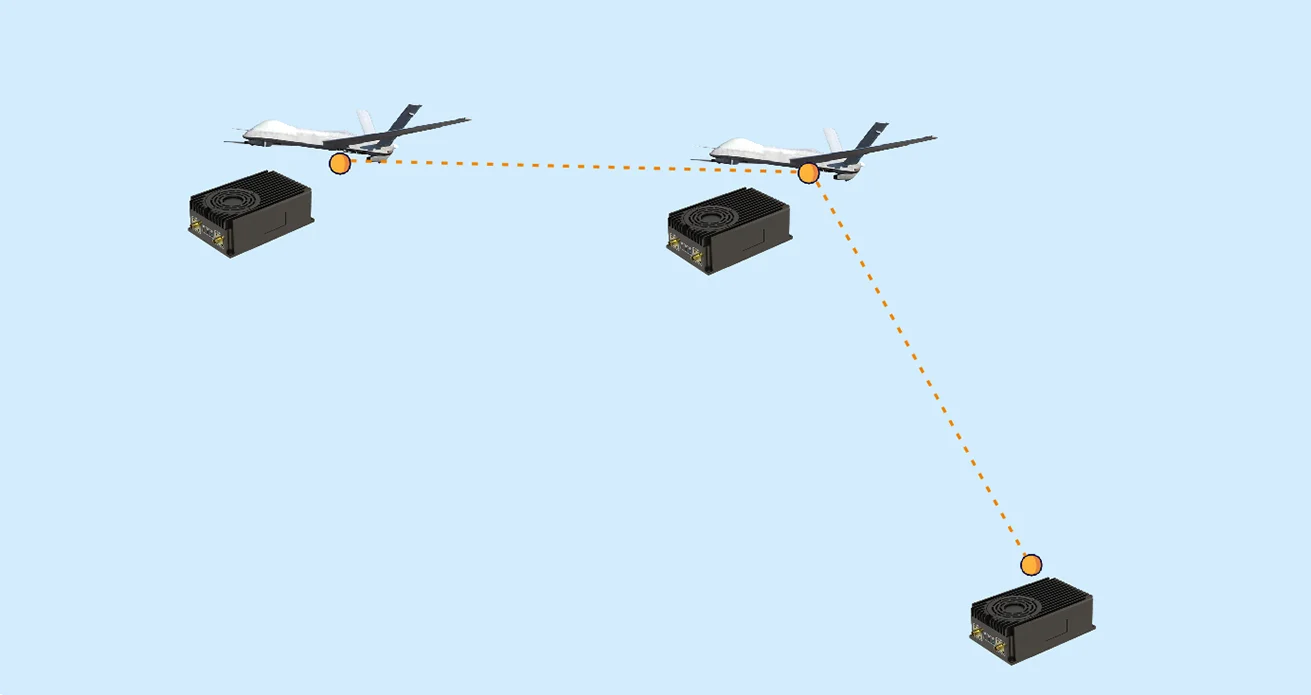
3. Antenna Type
The type and placement of antennas play a major role in maintaining signal quality:
-
Omnidirectional antennas radiate signals evenly in all directions, suitable for drones that move in various directions.
-
Directional antennas (patch or helical) focus signals in a particular direction, ideal for long-distance point-to-point transmission.
For long-range applications, a combination of high-gain directional antennas on the receiver and omnidirectional antennas on the drone often delivers optimal performance.
4. Latency
Latency refers to the delay between the camera capturing an image and it appearing on your screen. Long-range VTXs often introduce slightly higher latency due to signal processing. For casual aerial photography, a latency of 100–200ms may be acceptable, but for FPV racing or real-time drone control, minimizing latency is crucial.
5. Video Quality
Video resolution and clarity are essential for both piloting and post-processing. Modern long-range VTX units support HD video transmission, often up to 1080p, using advanced digital modulation techniques. Some high-end VTX units even support 4K video for professional filmmaking, though at the cost of increased power consumption and potential latency.
6. Compatibility and Control
Many long-range VTX units offer OSD (On-Screen Display) integration, allowing pilots to adjust VTX settings, power levels, and channel frequencies directly from the transmitter or via software. Some models also support smart features like auto frequency hopping to avoid interference automatically.
Selecting the Right Long-Range Drone Video Transmitter
Choosing the correct VTX depends on your specific use case. Here are some guidelines:
-
For professional aerial photography or filmmaking: Prioritize high-resolution video, low latency, and stable transmission. Digital VTX units such as DJI’s digital FPV system or other HD digital transmitters are excellent choices.
-
For FPV racing and freestyle: Focus on low latency and lightweight transmitters. Analog long-range VTX units often perform better in these scenarios.
-
For surveying, inspection, or industrial applications: Reliability and range are key. A high-power analog or digital VTX with robust antennas ensures a steady signal even in obstructed environments.
Installation and Best Practices
Proper installation of your long-range VTX significantly affects performance:
-
Mounting: Keep the transmitter away from high-current wires, ESCs, or batteries to minimize electromagnetic interference.
-
Antenna Placement: Position antennas vertically and away from the drone frame to avoid signal blockage. Ensure directional antennas on receivers are accurately pointed at the drone.
-
Heat Management: High-power transmitters generate heat. Use VTX units with heat sinks or active cooling for prolonged flights.
-
Frequency Planning: Check local frequency regulations and avoid overlapping channels with nearby drones or Wi-Fi devices.
Common Challenges with Long-Range Transmission
Even the best VTX units face challenges:
-
Signal Interference: Urban areas or crowded airspaces can disrupt video transmission. Using less crowded frequencies or higher-gain antennas can help.
-
Range Limitations: Environmental factors such as trees, buildings, and weather can reduce effective range. Always test your VTX in real-world conditions.
-
Battery Drain: High-power VTX units consume more energy, potentially reducing flight time. Consider using separate power sources if needed.
-
Legal Restrictions: Many countries regulate transmission power and frequencies. Operating outside these limits can result in fines or equipment confiscation.
Future Trends in Long-Range Drone Video Transmission
The industry is evolving rapidly. Emerging trends include:
-
Digital VTX Systems: Offering HD video, better error correction, and improved signal stability over longer distances.
-
Mesh Networks: Allowing multiple drones to relay video signals for ultra-long-range applications.
-
AI-Assisted Transmission: Intelligent signal optimization to avoid interference and maximize range automatically.
-
Lightweight and Compact Designs: Advanced materials and miniaturization reduce weight while maintaining performance.
Conclusion
Long-range drone video transmitters are a critical component for anyone looking to capture or stream video over extended distances. By understanding transmission power, frequency bands, antenna design, latency, and installation best practices, pilots can maximize their drone’s performance and achieve stunning results. Whether for professional cinematography, FPV racing, or industrial inspections, selecting the right long-range VTX ensures reliable, high-quality video transmission, allowing you to push the limits of your drone flights safely and effectively.
Investing in the right long-range drone video transmitter is more than just buying hardware—it’s about unlocking the full potential of your drone, expanding your operational range, and ensuring the clarity and reliability of every aerial shot.
www.suntor.com
suntor


Average Rating